Step 1:
Install beSTORM and an HTTPS server on two separate machines that are not otherwise in use or on a network.
Assign IP addresses to beSTORM server and target server like: 192.168.1.2 and 192.168.1.1
Connect the beSTORM server directly to the machine running the SSL server with a network cable, and no switch in the middle.
Step 2:
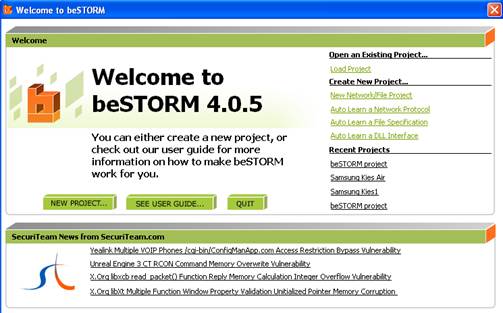
Start beSTORM on the client machine and click on the New Project button:
Step 3:
Give the project a name, accept all other defaults and click Next
Step 4:
From the list of modules, select HTTP/1.0 (SSL) or HTTP/1.1 (SSL). Set the Target Host Settings to be the IP of the SSL server and the Remote Port to the SSL port (usually 443).
Step 5:
(Optional) set the environment variables if needed.
Step 6:
If the SSL server is a Windows server, install the beSTORM monitor on it, run the monitor on the SSL server machine, attach it to the SSL process and put the IP of the remote machine on the Monitor Configuration page and select Remote Debugger.
Alternatively, if the SSL server is not accessible, on the ‘Monitor configuration’ page, select ICMP Echo and TCP Echo, and accept all other defaults.
Step 7:
Click ‘Finish’ to end the wizard and save settings as a Project. The testing will start automatically if the Auto-Start box is checked.
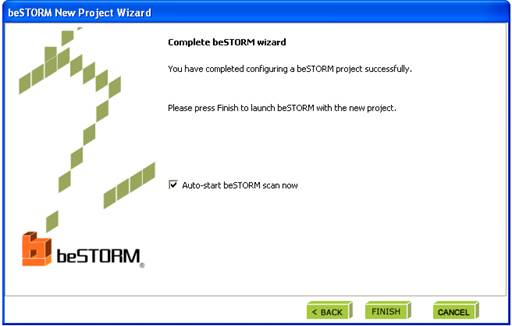
Step 8:
If an exception happens (an attack is successful) a message will pop up briefly to let you know the remote server is not responding.
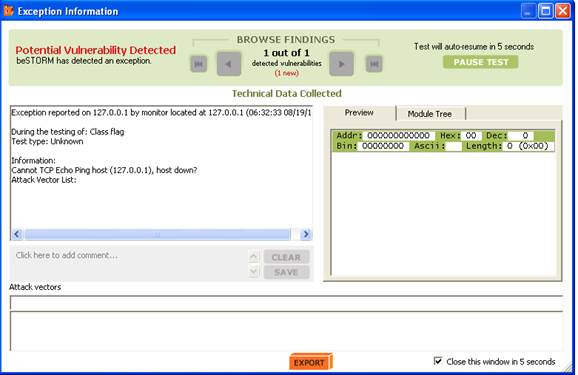
This indicates a possible vulnerability. Testing will resume in 5 seconds unless Pause Test is pressed.
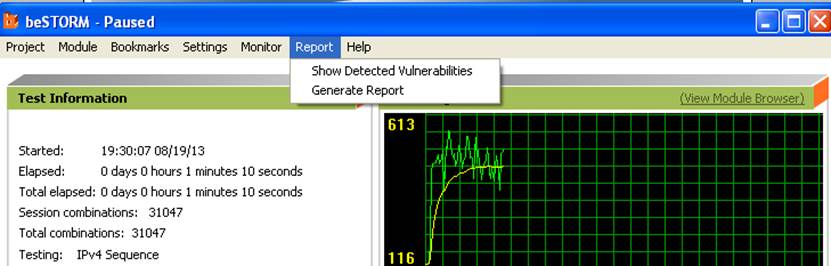
When the testing is finished, click on ‘Report’ to see a short report:
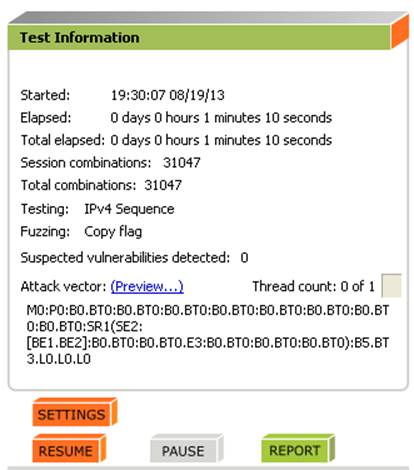
You can also select Report->Generate Report from the menu to generate a more complete report of the testing: